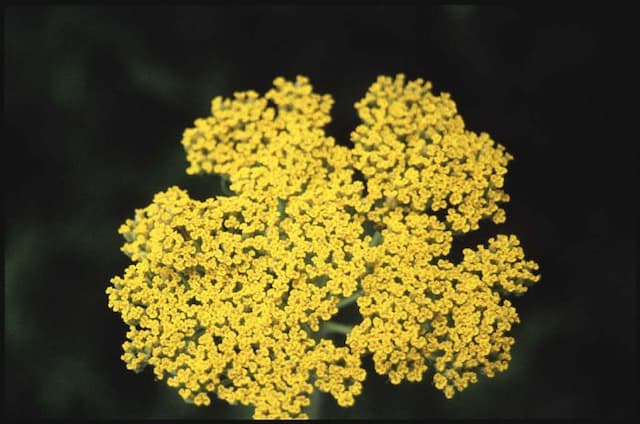
White Heath Aster Symphyotrichum ericoides 'Golden Spray'

ABOUT
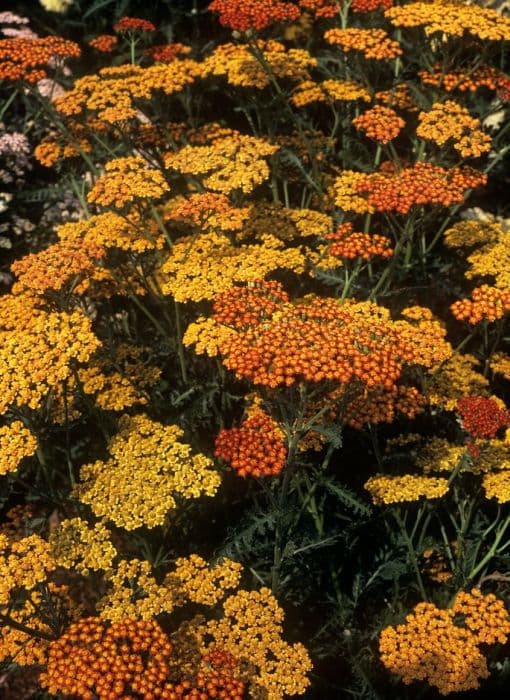
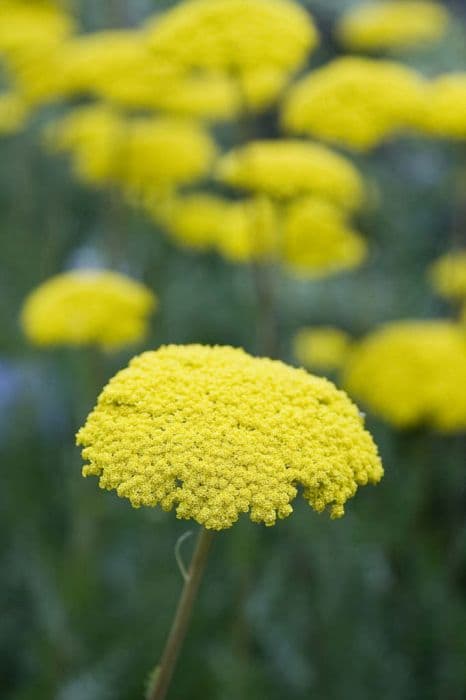
The plant known as Golden Spray is adorned with copious small, daisy-like flowers that boast a lively yellow hue, radiating a warm and cheerful ambience. Each flower is comprised of a dense cluster of yellow disk florets at its core, encircled by delicate and slender ray florets that sometimes exhibit hints of white, giving them a fresh and crisp look against the lush green foliage. The leaves of Golden Spray are narrow and linear, lending a fine-textured appearance to the plant. This texture is further complemented by the densely branched stems, which create a bushy and full-bodied silhouette, teeming with an abundance of blooms. The plant displays an overall airy and frothy character, reminiscent of golden clouds of flowers that seem to float above the greenery. The foliage remains healthy and vibrant, offering a verdant backdrop for the brilliant yellow flowers that continue to add color and life well into the autumn season, providing a lasting visual interest in the garden.
About this plant
 Names
NamesFamily
Asteraceae
Synonyms
White Heath Aster, Heath Aster, Golden Spray
Common names
Aster ericoides 'Golden Spray', Symphyotrichum pilosum 'Golden Spray', Eurybia ericoides 'Golden Spray'
 Toxicity
ToxicityTo humans
Heath aster is generally considered non-toxic to humans. There are no well-documented cases of toxicity from ingesting or coming into contact with this plant.
To pets
Heath aster is not known to be toxic to pets. It is generally considered safe for dogs, cats, and other household animals, and there are no common symptoms of poisoning associated with this plant. However, individual animals may have different sensitivities, and any plant material ingested in large quantities could cause gastrointestinal upset or other digestive issues.
 Characteristics
CharacteristicsLife cycle
Perennials
Foliage type
Deciduous
Color of leaves
Green
Flower color
Yellow
Height
3 feet (0.91 meters)
Spread
2 feet (0.61 meters)
Plant type
Herb
Hardiness zones
3-9
Native area
North America
Benefits
 General Benefits
General Benefits- Landscape Aesthetics: Symphyotrichum ericoides 'Golden Spray', commonly known as Heath Aster, provides visual interest with its golden-yellow flowers that can enhance garden landscapes.
- Attracts Pollinators: Heath Aster is known to attract butterflies, bees, and other pollinating insects, which are vital for the pollination of many plants.
- Drought Tolerant: Once established, this plant has a good drought tolerance, making it suitable for xeriscaping or dry garden areas.
- Easy to Grow: Heath Aster is considered to be low-maintenance, requiring minimal care once established, which is ideal for both novice and seasoned gardeners.
- Wildlife Habitat: It provides shelter and food resources for wildlife, particularly during the late summer and fall when other food sources may be scarce.
- Autumn Interest: Its late flowering period adds color and interest to the garden at a time when many other flowers have finished blooming.
- Soil Erosion Control: The root system of Heath Aster can help stabilize soil and prevent erosion, particularly in sloped areas of a garden.
- Winter Interest: Even after flowering, the dry stems and seed heads can provide visual interest in the winter garden landscape.
- Compact Growth: Its compact and bushy growth habit makes it suitable for borders, rock gardens, and as a filler plant among other perennial plants.
- Versatility: Its adaptability to a range of soil types and conditions make Heath Aster a versatile choice for different garden designs and locations.
 Medical Properties
Medical PropertiesThis plant is not used for medical purposes.
 Air-purifying Qualities
Air-purifying QualitiesThis plant is not specifically known for air purifying qualities.
 Other Uses
Other Uses- Floral Arrangements: Heath aster's fine textured flowers are popular in fresh and dried floral arrangements, adding a delicate touch to bouquets and decorations.
- Garden Borders: Their compact size and abundant blooms make heath asters suitable for garden borders, creating a dense display of late-season color.
- Butterfly Gardens: Heath asters are an excellent addition to butterfly gardens as they are a nectar source for a variety of butterflies, including monarchs and other pollinators.
- Rock Gardens: The plant's ability to thrive in well-drained soil makes it ideal for rock garden settings where it adds late-season interest.
- Erosion Control: The dense mat-like quality of heath asters can help stabilize soil and prevent erosion on slopes and banks.
- Photography: The vibrant golden blooms provide a picturesque backdrop for photographers, especially in natural light settings.
- Fall Interest: When most perennials are fading, heath asters add color and life to the fall garden, extending the visual interest in the landscape.
- Wildlife Habitat: The dense foliage can offer shelter for small wildlife, such as insects and ground-nesting birds.
- Thematic Gardening: Heath asters can be used in moon gardens due to their light-colored blooms that can reflect moonlight and create a luminous nighttime garden aspect.
- Companion Planting: Heath aster can be paired with other late-blooming perennials such as sedums and ornamental grasses for a layered garden design.
Interesting Facts
 Feng Shui
Feng ShuiThe Heath Aster is not used in Feng Shui practice.
 Zodiac Sign Compitability
Zodiac Sign CompitabilityThe Heath Aster is not used in astrology practice.
 Plant Symbolism
Plant Symbolism- Determination - Symphyotrichum ericoides, commonly known as Heath Aster, often symbolizes determination because of its ability to thrive in harsh conditions and poor soils.
- Patience - This plant blossoms in the late summer to fall, representing patience in waiting for the right moment to display its beauty.
- Elegance - The fine, needle-like foliage and numerous tiny flowers of the 'Golden Spray' variety give it an elegant appearance, hence symbolizing elegance and grace.
- New Beginnings - Heath Asters bloom at the end of the growing season, which is often interpreted as a symbol of new beginnings as it heralds the onset of autumn and the cycle of seasons.
 Water
WaterThe Heath Aster 'Golden Spray' should be watered early in the morning to allow the foliage to dry out during the day, reducing the risk of disease. It thrives with regular watering, approximately once a week, but this may need to be increased to every few days during dry spells or hot weather. Ensuring the soil is moist but not waterlogged is critical; typically, about 1 gallon of water per plant is sufficient each time you water. During the winter or in cooler climates, reduce watering as the plant's growth slows and its water requirements decrease.
 Light
LightThe Heath Aster 'Golden Spray' does best in full sun, receiving at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight daily. It can tolerate partial shade, but flowering will be more prolific in a location with ample sunshine. An ideal spot would be an area that offers bright, unfiltered daylight to encourage maximum bloom production.
 Temperature
TemperatureHeath Aster 'Golden Spray' can tolerate a temperature range, with minimum winter temperatures not dropping below 40 degrees Fahrenheit, ensuring that the plant remains hardy. It prefers growing in conditions where summer temperatures average between 75 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit. The maximum temperature should not consistently exceed 90 degrees Fahrenheit as prolonged heat can stress the plant.
 Pruning
PruningPruning the Heath Aster 'Golden Spray' encourages bushier growth and more blooms. Deadheading spent flowers throughout the blooming season can stimulate new blooms. Prune back the entire plant by one-third to one-half in early summer to delay blooming and control plant height. After the first frost in fall or early winter, cut back the dead stems to ground level to maintain a tidy appearance and prevent self-seeding.
 Cleaning
CleaningAs needed
 Soil
SoilThe best soil mix for Heath Aster, known as Symphyotrichum ericoides 'Golden Spray', is well-draining soil enriched with organic matter. The plant prefers a pH range of 6.0 to 8.0.
 Repotting
RepottingHeath Aster, or Symphyotrichum ericoides 'Golden Spray', should be repotted every 2 to 3 years to replenish the soil and encourage healthy growth.
 Humidity & Misting
Humidity & MistingHeath Aster, also Symphyotrichum ericoides 'Golden Spray', thrives in moderate humidity levels but is quite adaptable to various humidity conditions.
 Suitable locations
Suitable locationsIndoor
Place Heath Aster in bright, indirect light and ensure good air circulation.
Outdoor
Plant in full sun to partial shade with well-draining soil.
Hardiness zone
3-8 USDA
 Life cycle
Life cycleThe Symphyotrichum ericoides 'Golden Spray', commonly known as Heath Aster, begins its lifecycle as a seed, germinating in the spring when soil temperatures warm and moisture conditions are optimal. Upon germination, seedlings establish root systems and develop into vegetative plants, forming a rosette of leaves. During the growing season, it develops woody stems and fine foliage, reaching maturity and beginning to flower in late summer to fall when pollinators such as bees and butterflies are attracted to its abundant golden-yellow blooms. After pollination, the flowers produce seeds that are dispersed by wind or wildlife. As a perennial, the aboveground portions of the plant die back with the first frosts of winter, but the root system remains alive, lying dormant until the next spring when the cycle begins anew. Each year, the plant can also spread through its rhizomatous roots, gradually expanding its presence in a garden or natural area.
 Propogation
PropogationPropogation time
Early Spring
The most popular method of propagating the Heath Aster, or Symphyotrichum ericoides 'Golden Spray', is through division. This is ideally done in the spring when new growth begins to show, ensuring that the plant has the full growing season to establish. To propagate by division, carefully dig up the aster, ensuring you preserve as much root as possible. Gently separate the plant into smaller clumps, making sure each clump has several shoots and a good amount of root attached. Immediate replanting of the divisions in a well-prepared garden soil enriched with organic matter will give them the best start. Water the new plantings thoroughly to settle the soil around the roots and maintain even soil moisture until the new plants are established.