White Heath Aster Symphyotrichum ericoides 'Blue Star'

ABOUT
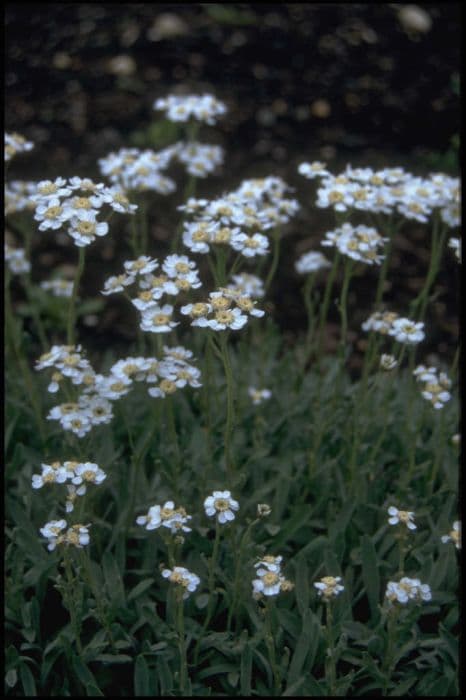
The 'Blue Star' aster is a perennial plant adorned with a profusion of small, daisy-like flowers. The flowers boast a charming light blue to lavender color and typically feature a yellow center that adds a striking contrast to the petals. This aster variant has a bushy and compact form, with numerous branching stems that create a full and mounded appearance. The leaves of 'Blue Star' aster are narrow and linear, resembling the fine texture of heather. They cover the stems densely, providing a feathery backdrop to the delicate blooms. These leaves are generally a medium green shade, contributing to the plant's overall lush look. As the plant enters its blooming season, it transforms into a mass of blue blossoms, creating the effect of a starry sky on the ground. The flowering period often occurs in the late summer to fall, extending the garden's color display into the cooler months when many other plants have finished blooming. The 'Blue Star' aster is a hardy plant, capable of withstanding different environmental conditions, making it a popular choice for gardeners looking to add long-lasting color and texture to their flowerbeds without worrying about extensive care requirements.
About this plant
 Names
NamesFamily
Asteraceae
Synonyms
White Heath Aster, Heath Aster, Blue Star
Common names
Aster ericoides 'Blue Star', Symphyotrichum pilosum var. ericoides 'Blue Star'.
 Toxicity
ToxicityTo humans
Heath aster is not known for its toxicity to humans. Generally, it is considered non-toxic, and there are no common symptoms associated with poisoning because it is not commonly regarded as a poisonous plant. However, individuals may have varying degrees of sensitivity to different plants, so while it's not known for being harmful, it's still advisable to avoid ingesting any plant not meant for consumption.
To pets
Heath aster is not known for its toxicity to pets. It is typically considered non-toxic to animals like cats and dogs, and there are no widespread reports of symptoms associated with poisoning from ingestion of this plant. As with humans, each pet may have individual sensitivities, but generally, the heath aster is not recognized as a dangerous plant for pets.
 Characteristics
CharacteristicsLife cycle
Perennials
Foliage type
Deciduous
Color of leaves
Green
Flower color
Blue
Height
1-3 feet (0.3-0.9 meters)
Spread
1-2 feet (0.3-0.6 meters)
Plant type
Herb
Hardiness zones
3-9
Native area
North America
Benefits
 General Benefits
General Benefits- Attracts Pollinators: The plant serves as an attractive food source for bees, butterflies, and other beneficial insects.
- Drought Tolerance: Once established, 'Blue Star' is quite resilient to drought conditions, making it suitable for xeriscaping.
- Erosion Control: Its root system helps stabilize soil, making it useful for controlling erosion in landscapes.
- Low Maintenance: This cultivar generally requires minimal upkeep, which can save time and resources.
- Aesthetic Appeal: 'Blue Star' adds visual interest to gardens with its fine textured foliage and bluish-lavender flowers.
- Wildlife Habitat: Provides cover and food for various small animals and insects, enhancing biodiversity.
- Seasonal Interest: It offers late summer to fall bloom, extending the garden's visual appeal into the cooler months.
- Adaptability: Can thrive in a range of soil types as long as they're well-draining, making it versatile for different gardens.
 Medical Properties
Medical PropertiesThis plant is not used for medical purposes.
 Air-purifying Qualities
Air-purifying QualitiesThis plant is not specifically known for air purifying qualities.
 Other Uses
Other Uses- Symphyotrichum ericoides 'Blue Star', more commonly known as Heath aster, can be used in dye production, with various plant parts yielding different colors.
- The dried stems of Heath aster can be incorporated into floral arrangements to provide a rustic aesthetic and long-lasting structure.
- Heath aster, when planted in mass, can serve as a living mulch, helping to retain soil moisture and suppress weeds.
- The fibrous roots of Heath aster can help in soil erosion control by stabilizing the soil, particularly on slopes and banks.
- Heath aster can be used as a companion plant in vegetable gardens to attract beneficial insects that prey on garden pests.
- When planted along borders or walkways, Heath aster serves an ornamental purpose, marking edges with its bright blue star-like flowers.
- The plant can be used for educational purposes in schools and nature centers to discuss pollination, as it attracts a wide variety of bees and butterflies.
- In photography and painting, the Heath aster provides a picturesque, natural backdrop during its blooming season in the fall.
- For xeriscaping, Heath aster is an ideal option because it is drought resistant and thrives in poor soil conditions.
- The plant's natural resistance to many deer and rabbit browsing makes Heath aster suitable for areas where these animals are a common problem.
Interesting Facts
 Feng Shui
Feng ShuiHeath Aster is not used in Feng Shui practice.
 Zodiac Sign Compitability
Zodiac Sign CompitabilityHeath Aster is not used in astrology practice.
 Plant Symbolism
Plant Symbolism- Diligence: Symphyotrichum ericoides 'Blue Star', commonly known as Heath Aster, requires little maintenance but continues to bloom vigorously, symbolizing persistent effort and hard work.
- Innocence: The delicate and dainty flowers of the Heath Aster are often associated with purity and innocence, reminiscent of a simpler, more carefree time.
- New beginnings: As asters often bloom in the fall, they can symbolize new beginnings or starting something new as other flowers are ending their blooming season.
- Patience: The Heath Aster is a symbol of patience, as it blooms later in the year when most other flowers have completed their cycle.
- Wisdom: The star-like shape of the blooms is sometimes seen as a symbol of wisdom and guidance.
 Water
WaterFor the Blue Star aster, water regularly to keep the soil consistently moist, especially during the first growing season to establish a deep, extensive root system. After establishment, they are somewhat drought tolerant and may only need watering every week or so, depending on climate conditions. It's best to water deeply, providing about 1 inch of water, which usually translates to about 0.6 gallons per square foot. Avoid overhead watering to prevent mildew and diseases, especially in humid climates, focusing the water at the base of the plant.
 Light
LightThe Blue Star aster thrives best in full sun conditions. It prefers a spot where it can receive at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight daily. While it can tolerate light shade, too much shade can lead to leggy growth and fewer flowers.
 Temperature
TemperatureBlue Star aster is hardy and can tolerate a wide range of temperatures, typically surviving winter lows to about -20°F and summer highs well into the 90°F. However, ideal growing conditions are within the 60°F to 75°F range, which promotes robust growth and flowering.
 Pruning
PruningPrune the Blue Star aster in late winter or early spring before new growth begins, cutting back the previous year's growth to about 4 to 6 inches. This will encourage bushier growth, more blooms, and help maintain a tidy shape. Deadheading spent flowers during the season will encourage continued blooming and prevent unwanted self-seeding.
 Cleaning
CleaningAs needed
 Soil
SoilThe best soil mix for Heath Aster 'Blue Star' is well-draining with a slightly acidic to neutral pH of 6.0 to 7.0. A mix of garden soil, compost, and perlite or sand provides good aeration and nutrient content, supporting healthy growth.
 Repotting
RepottingHeath Aster 'Blue Star' should be repotted every two to three years or when it outgrows its container to refresh the soil and encourage further growth.
 Humidity & Misting
Humidity & MistingHeath Aster 'Blue Star' thrives in average ambient humidity and does not require any special humidity adjustments, making it suitable for typical outdoor conditions.
 Suitable locations
Suitable locationsIndoor
Place in bright indirect light and ensure good air circulation.
Outdoor
Full sun to partial shade, well-draining soil, average water.
Hardiness zone
3-9 USDA
 Life cycle
Life cycleHeath Aster 'Blue Star' begins its life cycle as a seed, which germinates in late winter to early spring, depending on the climate. Seedlings emerge and grow into well-branched plants with narrow, linear leaves that form a bushy mound. Throughout the spring and summer, the plant continues to grow, focusing on vegetative development and root system expansion. In late summer to early fall, it enters the flowering stage, producing numerous small, blue to violet, daisy-like flowers with yellow centers that attract pollinators. Following pollination, the flowers develop into dry, seed-containing fruits called achenes, which are dispersed by wind, allowing the plant to spread. As winter approaches, the Heath Aster 'Blue Star' becomes dormant, with the aerial parts dying back, and relies on its perennial root system to survive the winter and regenerate the next spring.
 Propogation
PropogationPropogation time
Late summer
The Symphyotrichum ericoides 'Blue Star', commonly known as Heath Aster, can be propagated ideally during the late spring or early summer, coinciding with the period of active growth. The most popular method of propagation for Heath Aster is by division, wherein the gardener can gently separate a well-established clump into smaller sections. To do this, one should carefully dig up the plant cluster, making sure to keep a good portion of roots with each section. These sections should then be immediately transplanted into a well-prepared soil bed or pots, spaced adequately apart to allow for growth. It is essential to maintain adequate watering for the newly transplanted divisions until they are well-established, thus ensuring a higher success rate in the propagation of Heath Aster.