Schreber's aster Eurybia schreberi

ABOUT
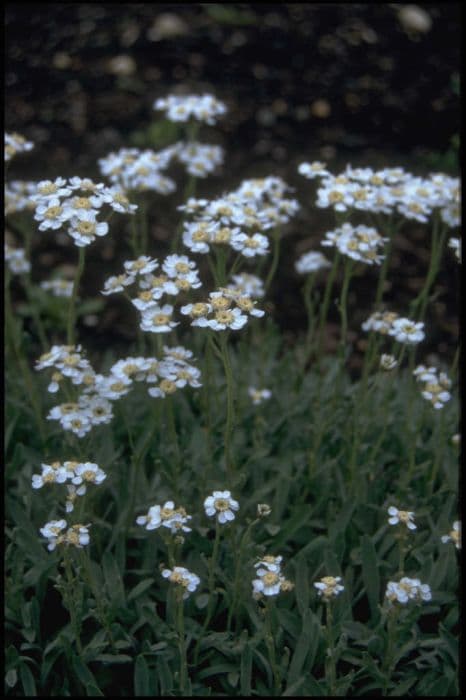
Eurybia schreberi, commonly known as the Schreber's aster, is a flowering plant that exhibits a bushy, clumping form. The leaves of this aster are typically heart-shaped at the base, becoming narrower and more lance-like as they ascend the stems. The foliage is known for its deep green color, providing a lush background for the flowers. The flowers of Schreber's aster are composed of a central disc, often a yellowish to reddish-brown, surrounded by numerous small, violet to purplish petals that radiate outward. These daisy-like flowers form a flat-topped array at the tip of the stems and are known to attract butterflies and other pollinators. The blooming period of this plant occurs in the late summer to fall, adding vibrant color to the landscape during this time. The stems of Schreber's aster are often rigid and hairy, with the plant displaying a branching habit that contributes to its overall dense and full appearance. This aster variety is a herbaceous perennial, meaning it dies back to the ground each winter and re-emerges from its root system in the spring. It can be a charming addition to gardens where its flowering can be appreciated up close or seen as part of a mixed border.
About this plant
 Names
NamesFamily
Asteraceae
Synonyms
Schreber's Aster, Eastern Wood Aster
Common names
Eurybia schreberi
 Toxicity
ToxicityTo humans
Eurybia schreberi, commonly known as Schreber's aster, is not widely recognized for its toxicity to humans. There is limited information regarding its potential poisonous effects. Ingesting any part of this plant is unlikely to result in significant toxic symptoms in humans.
To pets
Schreber's aster, the common name for Eurybia schreberi, similarly does not have a well-documented history of toxicity to pets. If pets ingest parts of this plant, they are not likely to experience severe symptoms of poisoning. However, it is always advisable to monitor pets for any signs of distress after ingesting unknown plant material and to consult a veterinarian if any adverse reactions occur.
 Characteristics
CharacteristicsLife cycle
Perennials
Foliage type
Deciduous
Color of leaves
Green
Flower color
Blue
Height
1-2 feet (30-60 cm)
Spread
1-2 feet (30-60 cm)
Plant type
Herb
Hardiness zones
4
Native area
North America
Benefits
 General Benefits
General Benefits- Ecosystem Support - Eurybia schreberi, commonly known as Schreber's Aster, offers food and habitat for pollinators like bees and butterflies, thus contributing to the ecological balance and biodiversity.
- Soil Stabilization - The root systems of Schreber's Aster help to stabilize soil, reducing erosion and improving soil health.
- Ornamental Value - With its attractive flowers, Schreber's Aster is used in gardens and landscaping for aesthetic purposes, adding color and beauty to natural settings.
- Wildlife Nourishment - The plant provides nectar and pollen sources for a variety of insects and seeds for birds, serving as an important food resource in wildlife gardens and natural areas.
- Education and Research - Schreber's Aster can be used in educational settings and research projects to study plant-pollinator interactions and native plant cultivation practices.
- Cultural Significance - Indigenous and local cultures may value the plant for its role in traditional practices and knowledge, contributing to cultural heritage and diversity.
 Medical Properties
Medical PropertiesThis plant is not used for medical purposes.
 Air-purifying Qualities
Air-purifying QualitiesThis plant is not specifically known for air purifying qualities.
 Other Uses
Other Uses- Eurybia schreberi, commonly known as Schreber's aster, can be used as a natural dye, providing colors from its leaves and petals for fabrics.
- The plant can serve as a teaching tool in educational settings, demonstrating plant biology and the life cycle of perennials.
- Schreber's aster is often included in butterfly gardens to attract pollinators due to its nectar-rich flowers.
- When planted in areas prone to soil erosion, the root system of Schreber's aster can help stabilize the soil.
- The seeds of the plant can be incorporated into homemade bird feed mixes, attracting various bird species to yards and gardens.
- As a hardy native plant, it can be used in rewilding projects to restore natural habitats and support biodiversity.
- Its vibrant flowers can be used for natural confetti at events, providing a biodegradable alternative to synthetic materials.
- Eurybia schreberi can be integrated into a sensory garden, providing visual and tactile experiences with its unique foliage and blooms.
- The dried stalks and leaves can be utilized in arts and crafts for creating eco-friendly home decor items.
- It can serve as a companion plant in vegetable gardens, helping to attract beneficial insects that can aid in pollinating crops.
Interesting Facts
 Feng Shui
Feng ShuiThe plant Eurybia schreberi, commonly known as Schreber's aster, is not used in Feng Shui practice.
 Zodiac Sign Compitability
Zodiac Sign CompitabilitySchreber's aster is not used in astrology practice.
 Plant Symbolism
Plant Symbolism- Resilience: Eurybia schreberi, also known as the Schreber's aster, often symbolizes resilience due to its ability to thrive in various conditions, particularly in shaded woodland environments.
- Persistence: The Schreber's aster's capability to persist through changing seasons and bloom annually can represent persistence and the idea of overcoming challenges.
- Diversity: With its variety of habitat and form, the Schreber's aster may represent diversity and adaptation, indicative of one's ability to adapt to different situations in life.
- Patience: The growth and blooming cycle of the Schreber's aster requires patience, mirroring the virtue of waiting for the right moment to act or express oneself.
 Water
WaterThe common name for Eurybia schreberi is Schreber's aster. This plant prefers consistent moisture and should be watered deeply once a week, allowing the soil to slightly dry out between waterings. During hotter spells or in well-draining soil, you might need to water twice a week. Each watering session should provide about 1 to 1.5 gallons of water, ensuring it reaches the roots without flooding the plant. Overhead watering should be avoided to prevent leaf diseases; instead, water at the base of the plant.
 Light
LightSchreber's aster requires full sun to partial shade to thrive. The ideal spot is where it can receive at least 4-6 hours of direct sunlight daily, but it can also tolerate slightly shaded conditions. Avoid placing it in deep shade, as this would reduce its vigor and blooming potential.
 Temperature
TemperatureSchreber's aster flourishes in a temperature range generally between 50°F and 75°F. It is cold-hardy and can survive minimum temperatures as low as -20°F, which makes it suitable for many temperate climates. However, consistently high temperatures above 85°F may stress the plant.
 Pruning
PruningPrune Schreber's aster to maintain its shape and encourage bushier growth. Deadhead spent flowers regularly to promote continued blooming throughout the season. Cut back the plant in late fall or early spring to allow for new growth. It is typically not necessary to prune more than once a year unless the plant becomes unruly.
 Cleaning
CleaningAs needed
 Soil
SoilCommon Wood Aster (Eurybia schreberi) thrives in a well-draining, loamy soil that is rich in organic matter. The ideal pH for this plant ranges between 5.5 to 7.0. A good soil mix could be composed of garden soil, compost, and perlite or coarse sand to ensure proper drainage.
 Repotting
RepottingCommon Wood Aster (Eurybia schreberi) typically doesn't require frequent repotting and can be repotted every 2-3 years, or when it outgrows its current container.
 Humidity & Misting
Humidity & MistingCommon Wood Aster (Eurybia schreberi) prefers moderate to high humidity levels. Although it is adaptable, maintaining a humidity level of around 40-60% is considered ideal for this plant.
 Suitable locations
Suitable locationsIndoor
Provide bright indirect light and water when topsoil is dry.
Outdoor
Plant in partial shade and moist, well-draining soil.
Hardiness zone
3-8 USDA
 Life cycle
Life cycleEurybia schreberi, also known as Schreber's aster, begins its life cycle as a seed, which upon finding a suitable environment will germinate and develop into a small seedling. The seedling grows through the vegetative stage, forming leaves and roots, and eventually becomes a mature plant. During the growing season, Schreber's aster undergoes flowering, which is its reproductive stage; the plant produces flowers with both male and female components for pollination. After pollination, typically by insects, the flowers produce seeds, which are then dispersed by various means such as wind or animals. Once the seeds land in a favorable location, the cycle recommences with germination. The plant also spreads by producing offsets or rhizomes, thereby increasing its population through vegetative reproduction.
 Propogation
PropogationPropogation time
Spring-Early Summer
Propogation: The most popular method of propagation for Eurybia schreberi, commonly known as Schreber's Aster, is through seed sowing. Seeds can be sown outdoors in fall, which allows for natural stratification through the winter months, or started indoors before the last frost. For indoor starts, seeds should be cold stratified for about 1-2 months at temperatures near 40 degrees Fahrenheit (4.4 degrees Celsius). After stratification, seeds can be sown on the surface of a soil mix, as they require light for germination, and kept moist until they sprout. Once seedlings are large enough to handle and the danger of frost has passed, they can be transplanted outdoors to their final growing positions.