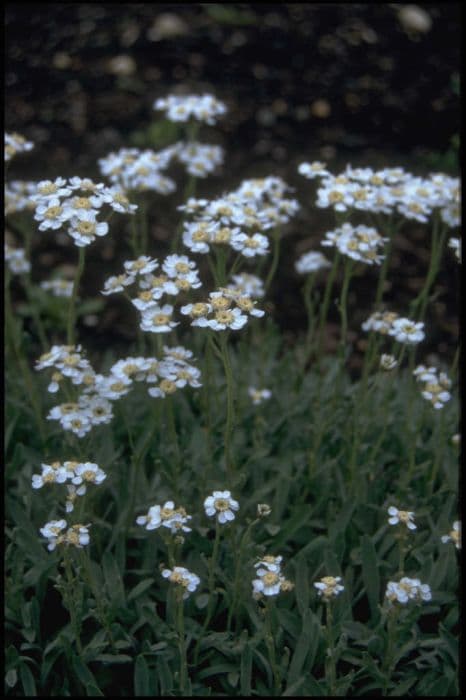
Stokes' Aster 'Mel's' Stokesia laevis 'Mel's' (PBR)
ABOUT
An upright, clump forming semi evergreen perennial with leathery, soft spiney dark green leaves. Large fringed violet-blue flowers are produced in the summer
About this plant
 Names
NamesFamily
Asteraceae
Synonyms
Stokes' Aster, Stokesia
Common names
Stokesia laevis 'Mel's Blue', Stokesia laevis 'Honeysong Purple'.
 Characteristics
CharacteristicsLife cycle
Perennials
Foliage type
Evergreen
Color of leaves
Green
Flower color
Blue
Height
1-2 feet (30-60 cm)
Spread
1-2 feet (30-60 cm)
Plant type
Herb
Hardiness zones
5-10
Native area
Southeastern United States
Benefits
 General Benefits
General Benefits- Attracts Pollinators: Stokes' Aster is known to attract bees and butterflies, which are beneficial for pollination.
- Drought Resistance: Once established, it is relatively tolerant of drought, requiring minimal watering in well-drained soils.
- Low Maintenance: Stokes' Aster is generally easy to care for, with limited requirements for fertilizing and pruning.
- Long Blooming Period: It often has a long flowering season, providing visual interest throughout the summer and sometimes into fall.
- Winter Interest: The seed heads can add texture and interest to the winter garden when left unpruned.
- Deer Resistance: The plant is known to be deer resistant, making it a suitable choice in areas with deer pressure.
- Compact Size: Stokes' Aster has a compact and clumping habit, ideal for borders, containers, and small gardens.
- Colorful Flowers: It produces attractive blue or violet flowers that can add a splash of color to garden landscapes.
- Cutting Garden: The flowers are suitable for cutting and can be used in floral arrangements.
- Soil Adaptability: It is adaptable to a range of soil types, although it prefers well-drained soil.
 Medical Properties
Medical PropertiesThis plant is not used for medical purposes.
 Air-purifying Qualities
Air-purifying QualitiesThis plant is not specifically known for air purifying qualities.
 Other Uses
Other Uses- Stokes' aster can be used as a natural fabric dye, with its petals providing shades of blue and purple when processed correctly.
- In art, the vibrant colors of the Stokes' aster can be pressed and incorporated into pressed flower crafts or botanical prints for decoration.
- The dried flowers of the Stokes' aster can be included in potpourri mixes for their aesthetic appeal and to add bulk to the mixture.
- Gardeners sometimes use Stokes' aster in companion planting to help attract beneficial insects like pollinators which can enhance the growth of vegetable crops and fruits.
- Stokes' aster seeds can be used for educational purposes, such as in school projects to teach children about plant life cycles and how seeds germinate.
- The sturdy stems of Stokes' aster can be utilized in basketry, being woven together to create intricate and decorative patterns.
- Because Stokes' aster blooms late in the season, it may serve as a valuable food source for migrating butterflies and insects preparing for winter.
- The flowers of Stokes' aster are sometimes used in the culinary world as an edible garnish, providing an unusual pop of color on plates.
- In photography and cinematography, the Stokes' aster can be chosen for its striking appearance to add visual interest in garden and nature scenes.
- Creative landscaping uses Stokes' aster in 'green roofs' or rooftop gardens where their low maintenance and drought resistance are valuable traits.
Interesting Facts
 Feng Shui
Feng ShuiThe Stokes' Aster is not used in Feng Shui practice.
 Zodiac Sign Compitability
Zodiac Sign CompitabilityThe Stokes' Aster is not used in astrology practice.
 Plant Symbolism
Plant Symbolism- Enduring Grace: Stokesia laevis, commonly known as Stokes' aster, is a plant that maintains its vibrant beauty throughout the blooming season, symbolizing grace that withstands time and circumstance.
- Natural Elegance: With its lush, attractive flowers, Stokes' aster represents a simple yet refined beauty, akin to an effortless elegance found in nature.
- Uniqueness: The variety 'Mel's Blue' with its distinct color and form suggests the value of individuality and the beauty in being one-of-a-kind.
- Cherishing Memories: Often used in cottage gardens, Stokes' aster can evoke nostalgia and symbolize cherished memories of past times and places.
- Prosperity: In some cultures, flowering plants like Stokes' aster are associated with growth and abundance, representing prosperity in one’s life.
 Water
WaterThe Stokes' aster should be watered regularly, aiming to keep the soil consistently moist without becoming waterlogged. Depending on the climate and weather conditions, this generally equates to about 1 inch of water per week. During hotter, dry spells, watering frequency should increase, with a thorough soaking that reaches deep into the root zone. It's best to water this plant in the morning to allow leaves to dry out over the course of the day, reducing the risk of fungal diseases.
 Light
LightThe Stokes’ aster thrives in full sun to partial shade conditions. For optimal growth and flowering, place it in a spot that receives at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day. However, some afternoon shade can be beneficial in very hot climates to prevent leaf scorch.
 Temperature
TemperatureStokes' asters are resilient down to temperatures of around 10 degrees Fahrenheit, making them suitable for a range of climate zones. They can typically survive up to 90 degrees Fahrenheit, but their ideal growing temperatures are between 60 and 80 degrees Fahrenheit. Provide some shade during the hottest part of the day if temperatures consistently exceed these limits to prevent heat stress.
 Pruning
PruningPruning is important for the Stokes’ aster to maintain its shape and promote vigorous growth. Deadhead spent flowers regularly to encourage further blooming. After the first killing frost in autumn, cut back the entire plant to about 2 to 3 inches above ground level to prepare it for winter. Prune again in early spring to remove any dead or damaged growth.
 Cleaning
CleaningAs needed
 Soil
SoilStokes' Aster prefers well-draining soil mixed with organic matter, such as compost or peat moss, to retain moisture without becoming waterlogged. The ideal pH range for Stokes' Aster is slightly acidic to neutral, approximately 5.5 to 6.5.
 Repotting
RepottingStokesia laevis 'Mel's', or Stokes' Aster, thrives when repotted every 2-3 years. Regular repotting helps refresh the soil and promotes healthy root growth without allowing the plant to become root-bound.
 Humidity & Misting
Humidity & MistingThe best humidity conditions for Stokes' Aster are moderate. It doesn't require high humidity and can do well in typical outdoor conditions, as excessive humidity can lead to fungal issues.
 Suitable locations
Suitable locationsIndoor
Place in bright, indirect light with good airflow.
Outdoor
Provide full sun to partial shade and protect from strong winds.
Hardiness zone
5-10 USDA
 Life cycle
Life cycleStokesia laevis 'Mel's', commonly known as the Stokes' aster, begins its life cycle when its seeds germinate, typically in early spring, as temperatures rise and conditions favor growth. The seedlings develop into rosettes of leaves at ground level, and over time, these rosettes enlarge and the plant forms a sturdy root system. In its flowering stage, usually by mid to late summer, it produces attractive flowers atop long stems, which can be blue, purple, pink, or white depending on the cultivar. After pollination, usually by insects, the flowers will produce seeds, which mature and are eventually dispersed near the parent plant or farther away by wind or animals. Once the flowering and seed-setting cycle is complete, the plant may enter a period of dormancy, especially in regions with colder winters, dying back to the ground level. In the following growing season, the plant will resume growth from its rootstock, repeating its life cycle.
 Propogation
PropogationPropogation time
Early Spring
Propogation: Stokesia laevis 'Mel's Blue', commonly known as Stokes' aster, is typically propagated through division, ideally during the early spring or fall when temperatures are mild. The most popular method of propagation is division, which ensures that the offspring plants will be true to the parent plant in terms of characteristics. To propagate by division, dig up the mature plant gently, ensuring you keep a good amount of roots intact. Then, using a sharp spade or knife, divide the root ball into smaller sections, each with several shoots and a portion of the root system. These divisions can then be replanted immediately at the same depth they were previously growing, about 12 to 18 inches (30 to 45 cm) apart to ensure adequate room for growth. The soil should be kept moist but not waterlogged to encourage establishment. This method allows gardeners to create new plants quickly and efficiently while maintaining the unique qualities of the 'Mel's Blue' cultivar.