Wormwood 'Lambrook Mist' Artemisia absinthium 'Lambrook Mist'

ABOUT
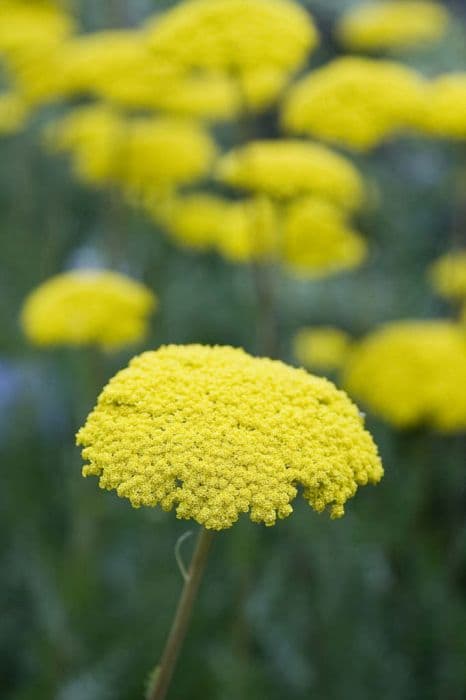
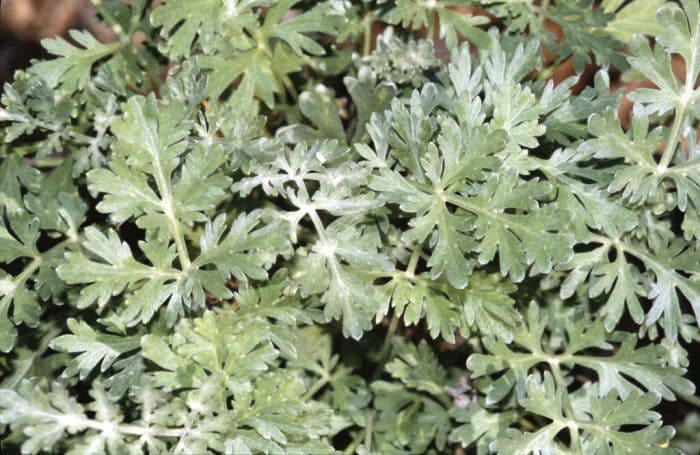
'Lambrook Mist' is an erect, woody-based perennial to 1m tall, with aromatic silvery-grey leaves to 15cm long, finely divided into very slender lobes, and slender sprays of small, dull yellow flower heads in late summer
About this plant
 Names
NamesFamily
Asteraceae.
Synonyms
Wormwood, Absinthe Wormwood, Grand Wormwood, Absinthium, Green Ginger.
Common names
Artemisia absinthium 'Lambrook Mist'.
 Characteristics
CharacteristicsLife cycle
Perennials
Foliage type
Deciduous
Color of leaves
Silvery-green
Height
2-3 feet (60-90 cm)
Spread
2 feet (60 cm)
Plant type
Herb
Hardiness zones
4-9
Native area
Europe
Benefits
 General Benefits
General Benefits- Ornamental Value: Artemisia absinthium 'Lambrook Mist', commonly known as Wormwood, adds aesthetic appeal to gardens with its fine-textured, silvery foliage and misty appearance.
- Drought Tolerance: Once established, Wormwood is highly drought-resistant, making it suitable for xeriscaping or gardens with low water availability.
- Pest Deterrent: The strong scent of Wormwood is known to repel various garden pests, acting as a natural deterrent without the need for chemical repellents.
- Erosion Control: Wormwood can help stabilize soil and prevent erosion due to its hardy and robust growing habits.
- Companion Planting: When used in companion planting, Wormwood can benefit nearby plants by deterring pests and potentially improving soil quality.
- Low Maintenance: This plant requires minimal care once established, making it ideal for gardeners who prefer low-maintenance landscapes.
- Wildlife Attraction: While it repels pests, the Wormwood plant may attract beneficial insects, which can contribute to the ecological balance of a garden.
- Adaptable: Wormwood can thrive in a range of soil conditions, from poor to moderately fertile, and can tolerate various climates.
- Seasonal Interest: This particular cultivar of Wormwood can provide visual interest throughout the growing season and even adds winter texture when many other plants have died back.
- Hedge or Border Plant: Due to its height and dense growth, Wormwood can be used effectively as a hedge or border plant to define garden spaces.
- Culinary Use: Though this list is excluding medicinal properties, it's worth noting that Wormwood has a history of use in culinary applications, particularly in flavoring spirits and bitters.
 Medical Properties
Medical Properties- Antiseptic: Historically used for its antiseptic properties to help cleanse wounds.
- Antispasmodic: Can provide relief from muscle spasms and stomach issues.
- Antihelminthic: Used traditionally to expel parasitic worms and other internal parasites.
- Antimalarial: Contains compounds like artemisinin, which have been used to treat malaria.
- Bitter tonic: Acts as a digestive stimulant and can improve appetite and digestion.
- Menstrual cycle regulator: Has been used to induce menstruation and ease dysmenorrhea.
 Air-purifying Qualities
Air-purifying QualitiesThis plant is not specifically known for air purifying qualities.
 Other Uses
Other Uses- Wormwood 'Lambrook Mist' can be used as a natural insect repellent in gardens to protect other plants due to its strong aromatic compounds.
- Dried wormwood leaves can serve as a moth deterrent when placed in wardrobes or drawers, keeping clothes free from moth damage.
- A concentrated infusion of wormwood can be applied to unsealed wood as a natural wood preservative and to prevent woodworm.
- The plant is sometimes used in companion planting to enhance the growth and flavor of vegetables like carrots and tomatoes.
- Wormwood can be included in compost activator mixes to speed up the decomposition process due to its high nitrogen content.
- Some artists use the plant in the preparation of natural green pigments for painting due to its chlorophyll-rich leaves.
- The distinct silvery foliage of wormwood is used in ornamental dry flower arrangements for its aesthetic value and longevity.
- Wormwood can be used to create a natural garden pathway barrier as its strong scent can deter small animals from crossing.
- The plant's bitter taste makes it useful as a natural deterrent for domestic animals to discourage them from chewing on garden plants or furniture.
- In the past, wormwood has been used to flavor and preserve beer before the widespread use of hops.
Interesting Facts
 Feng Shui
Feng ShuiThe Wormwood is not used in Feng Shui practice.
 Zodiac Sign Compitability
Zodiac Sign CompitabilityThe Wormwood is not used in astrology practice.
 Plant Symbolism
Plant Symbolism- Protection: Historically, Artemisia absinthium, commonly known as wormwood, was thought to ward off evil spirits and misfortune. It was often used in rituals and amulets for protection.
- Healing: Known for its medicinal properties, wormwood has been used to remedy various ailments, symbolizing healing and physical well-being.
- Bitterness: The plant’s bitter flavor lends to its symbolic association with bitterness and sorrow in life, often reminding individuals of the harsher aspects of existence.
- Absence: In the language of flowers, wormwood can represent absence or the loss of something or someone.
- Creativity: The use of wormwood in the production of absinthe, a spirit associated with artists and writers, imbues it with the symbolic meaning of inspiration and creativity.
 Water
WaterWormwood 'Lambrook Mist' is drought-tolerant once established and should be watered deeply but infrequently. The goal is to encourage a deep root system. Typically, watering once a week with about 1.5 gallons per plant during the active growing season is sufficient, but this may vary with local weather conditions. It is vital to reduce the frequency of watering as the plant matures and to allow the soil to dry out between waterings. Overwatering can lead to root rot, so it is better to err on the side of too dry rather than too wet.
 Light
LightWormwood 'Lambrook Mist' prefers full sun conditions to thrive. It should be planted in a spot where it receives at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. The more sun it gets, the better it will flower and the more vibrant its foliage will remain. If it is grown in partial shade, it may become leggy and produce fewer flowers.
 Temperature
TemperatureWormwood 'Lambrook Mist' can tolerate a wide range of temperatures but grows best in climates where the temperature remains consistently between 60 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit. It can survive minimum temperatures down to around 0 degrees Fahrenheit. It is hardy in USDA zones 4 through 9, indicating a good level of cold resistance, but it should be protected from extreme heat.
 Pruning
PruningWormwood 'Lambrook Mist' should be pruned to maintain its shape and encourage bushy growth. The best time to prune is in the early spring before new growth begins. It can also be cut back in the fall to prepare for winter. Typically, pruning once a year is sufficient, but if the plant becomes overgrown or woody, a second, lighter prune can be done in the summer after the first flush of growth.
 Cleaning
CleaningAs needed
 Soil
SoilWormwood 'Lambrook Mist' thrives in well-drained soil with full sun exposure. A soil mix with equal parts of loam, peat, and sharp sand ensures good drainage. Aim for a soil pH between 6.0 and 7.0.
 Repotting
RepottingWormwood 'Lambrook Mist' typically does not need frequent repotting. Repot every 2 to 3 years or when the plant seems root-bound or the soil appears exhausted.
 Humidity & Misting
Humidity & MistingWormwood 'Lambrook Mist' prefers low to moderate humidity levels and can tolerate dry air well, making it suitable for typical indoor environments.
 Suitable locations
Suitable locationsIndoor
Place in direct sunlight and avoid overwatering.
Outdoor
Full sun, well-drained soil; shelter from strong winds.
Hardiness zone
4-9 USDA
 Life cycle
Life cycleArtemisia absinthium 'Lambrook Mist', commonly known as Wormwood 'Lambrook Mist', starts its life as a seed, which germinates in the spring when soil temperatures and moisture levels are appropriate. Upon germination, seedlings emerge and begin to develop a rosette of deeply divided, silvery-grey foliage typical of the cultivar. As the plant matures, it undergoes vegetative growth, forming a robust bush with stems that can reach up to 1.5 meters tall, with the foliage becoming more pronounced and feathery. The next stage is the flowering period, which occurs in the late summer; tiny, pale-yellow flowers appear in clusters, though they are often considered inconspicuous compared to the ornamental foliage. After flowering, seed production begins, and as the seeds mature, they are dispersed by wind or wildlife, thus completing the reproductive cycle. As a perennial, the above-ground portions of Wormwood 'Lambrook Mist' die back in winter, but the plant can regrow from its root system the following spring, continuing its life cycle for several years.
 Propogation
PropogationPropogation time
Spring to Early Summer
Artemisia absinthium 'Lambrook Mist', commonly known as wormwood, is often propagated through division, which is the most popular method for this variety. The best time for division is in the spring when the plant begins to show new growth. To propagate wormwood by division, carefully dig up an established plant and use a sharp spade or knife to divide the root ball into several sections, each with a portion of the root system and some shoots. These divisions should then be replanted at the same depth they were growing at originally, spaced about 18 inches (approximately 45.72 centimeters) apart to allow for mature growth. Water the new divisions thoroughly after planting to encourage root development. This simple vegetative propagation method not only helps to expand your garden but can rejuvenate older plants that have become woody or less vigorous.